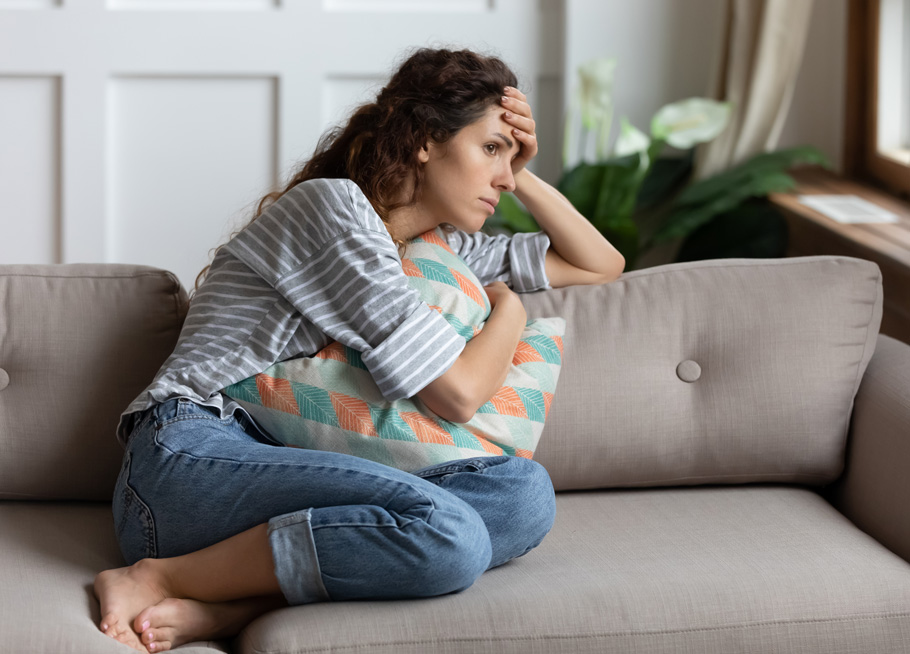
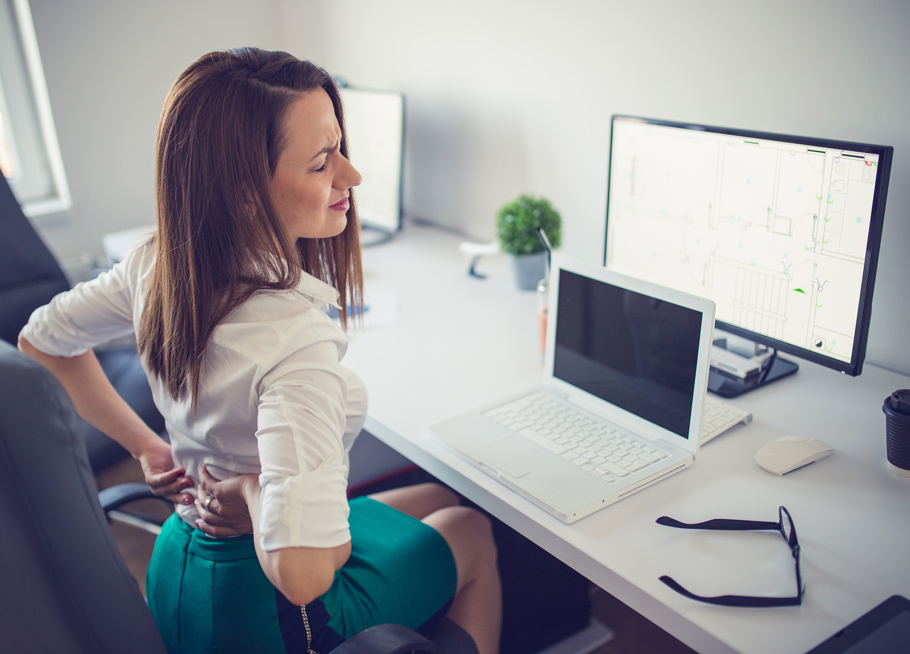
With the pressures and strains of modern life, the link between stress and joint pain is becoming more and more apparent. Joint pain is an issue that affects people of all backgrounds, whether as a result of an arthritic condition such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, or another condition where pain in the joints is a symptom, such as fibromyalgia.
Joint pain can lead individuals to seek various medical interventions, including medication and surgery. However, one crucial, yet frequently overlooked, aspect of addressing joint pain is stress management. Stress plays a significant role in the overall management of joint pain, and understanding the link between the two is vital for effective pain control.
The Impact Of Stress On Joint Pain
While there has been an increase in publicly available information about stress and how it affects health, much of it centres on mental well-being and cardiovascular health. Therefore, while individuals with joint pain might be aware of stress in their lives and that it should be addressed, they may not realise how directly it impacts their joints. Here is an overview:
Non-inflammatory arthritis and other joint pain
Stress triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response, releasing hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. While this response is beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress keeps the body in a heightened state of tension, leading to muscle tightness and increased joint pain. For individuals with conditions like osteoarthritis and other types of non-inflammatory arthritis, chronic stress can exacerbate muscle tension around the joints, increasing pain and discomfort.
Inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune conditions
Inflammatory autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, lupus, and even conditions like diabetes and thyroid problems (both of which can cause joint pain) are particularly sensitive to stress. Stress can trigger inflammation, leading to flare-ups and worsening symptoms.
It should also be noted that stress and joint pain can form a vicious cycle. An individual with pain in their joints may experience stress in response to the pain, and then that pain may become worse as a result of high stress levels. However, it is possible to break this cycle by committing to a stress and pain management routine.
How To Address Stress For The Management Of Joint Pain
Addressing stress should be a daily priority. While occasional relaxation, like going on a holiday, can help in the short term, consistent daily stress management practices are highly important. Incorporating activities such as yoga, meditation, and tai chi into your routine can significantly reduce stress levels. Even simple activities like daily walks or engaging in hobbies can provide substantial relief.
Meditation, in particular, is highly effective. Just 20 minutes of meditation each day can help reduce stress and contribute to overall pain management. For those who may not enjoy traditional stress management techniques, finding alternative activities that bring joy and relaxation is essential. The goal is to create a daily routine that incorporates stress reduction, which can form a core part of your pain management strategy.
The Influence Of Exercise And Diet On Stress And Joint Pain
Exercise and a healthy diet are fundamental components of managing stress and joint pain, as the foods we consume and our activity levels can have a direct impact on both.
Exercise
Regular physical activity helps keep muscles and joints strong and flexible, thereby reducing pain and improving overall health. It also encourages the release of endorphins – the body’s natural mood elevators – and regulates the level of stress hormones in the body.
Diet
A balanced diet supports overall joint health through consuming key vitamins and minerals, and can help with weight control, which in turn reduces stress on the joints. Meanwhile, it can help enhance cognitive function, regulate mood-affecting blood sugar levels, and support the production of mood-regulating serotonin, all of which can contribute to lower stress levels.
Combining exercise and a healthy diet with stress management practices creates a holistic approach to managing joint pain. This approach is particularly important for those with autoimmune conditions, as it can reduce the need for medications that modulate the immune system.
Medical Interventions For Stress
In some cases, patients with a history of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety, may benefit from seeing a psychiatrist to help manage their stress if they are finding it difficult to manage themselves. A psychiatrist may prescribe talking therapies or counselling, or medications such as duloxetine, which is a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) commonly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalised anxiety disorder.
However, this medication should not be the sole reliance in regards to stress management and joint pain. It is most effective when used in conjunction with lifestyle changes and other strategies outlined above.
Stress And Health: Joint Pain And The Bigger Picture
Stress management is not only crucial for dealing with joint pain, but also for improving overall health. Chronic stress is a major driver of a range of medical conditions, so by managing stress effectively, we can improve not only our joint health but other areas of our physical and mental wellbeing, potentially leading to longer, healthier lives. Prioritising stress management is not just beneficial – it’s essential.
Contact Dr Naveen Bhadauria on 0207 126 7264 or visit our contact page for more details.
Article by Dr. Naveen Bhadauria